

微信公众号

编辑部微信号
旅游导刊 ›› 2024, Vol. 8 ›› Issue (5): 76-109.DOI: 10.12054/lydk.bisu.263
收稿日期:2023-07-02
修回日期:2024-05-11
出版日期:2024-10-30
发布日期:2024-11-06
通讯作者:
欧阳旻(1996— ),男,湖南永州人,湘潭大学商学院博士研究生,研究方向为旅游地理、旅游经济运行等, E-mail:214180257@qq.com。作者简介:马丽君(1981— ),男,山东临沂人,博士,湘潭大学商学院教授、博士生导师,研究方向为旅游地理、旅游经济运行等;基金资助:
MA Lijun, OUYANG Min( ), LIANG Xiaoyao
), LIANG Xiaoyao
Received:2023-07-02
Revised:2024-05-11
Online:2024-10-30
Published:2024-11-06
摘要:
本研究收集了我国2019年入境旅游流的有关数据,构建入境旅游流循环分析指标,利用自然断点法、社会网络分析法、QAP分析法,揭示我国入境旅游流循环的空间分布特征及影响因素,结果发现:(1)存在117个省际入境旅游流循环、25个经济区间入境旅游流循环以及7个经济区内入境旅游流循环,涉及26个省区市。(2)入境旅游流循环强度的空间分布表现为“东高西低”,流量规模匹配度呈“高分散、低集聚”的空间分布格局,高、中、低3个等级的流向偏好匹配度均集中在中东部地区。(3)省际、区域间、区域内入境旅游流循环类型的数量和空间分布特征存在一定差异。多数入境旅游流循环的强度、流量规模匹配度、流向偏好匹配度不高,反映了我国入境旅游流循环质量不高,有待提升。(4)入境旅游流循环网络呈现出“东密西疏”的空间分布特征,整体网络密度较低。(5)交通便捷程度、对外经济贸易、旅游资源禀赋、经济发展水平和旅游接待能力均是影响入境旅游流循环的重要因素,各因素对入境旅游流循环强度、流量规模匹配度和流向偏好匹配度的影响不同。
中图分类号:
马丽君, 欧阳旻, 梁逍遥. 我国入境旅游流循环空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 旅游导刊, 2024, 8(5): 76-109.
MA Lijun, OUYANG Min, LIANG Xiaoyao. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Inbound Tourism Flow Circulation in China[J]. Tourism and Hospitality Prospects, 2024, 8(5): 76-109.
| 位置内部的关系比例Proportion of internal relationship in location | 位置接收到的关系比例Proportion of relationships received by location | |
|---|---|---|
| ≈0 | >0 | |
| ≥(gk-1)/(g-1) | 双向溢出板块 | 主受益板块 |
| ≤(gk-1)/(g-1) | 主溢出板块 | 经纪人板块 |
表1 块模型的板块划分标准
Tab. 1 Plate division criteria of the block model
| 位置内部的关系比例Proportion of internal relationship in location | 位置接收到的关系比例Proportion of relationships received by location | |
|---|---|---|
| ≈0 | >0 | |
| ≥(gk-1)/(g-1) | 双向溢出板块 | 主受益板块 |
| ≤(gk-1)/(g-1) | 主溢出板块 | 经纪人板块 |
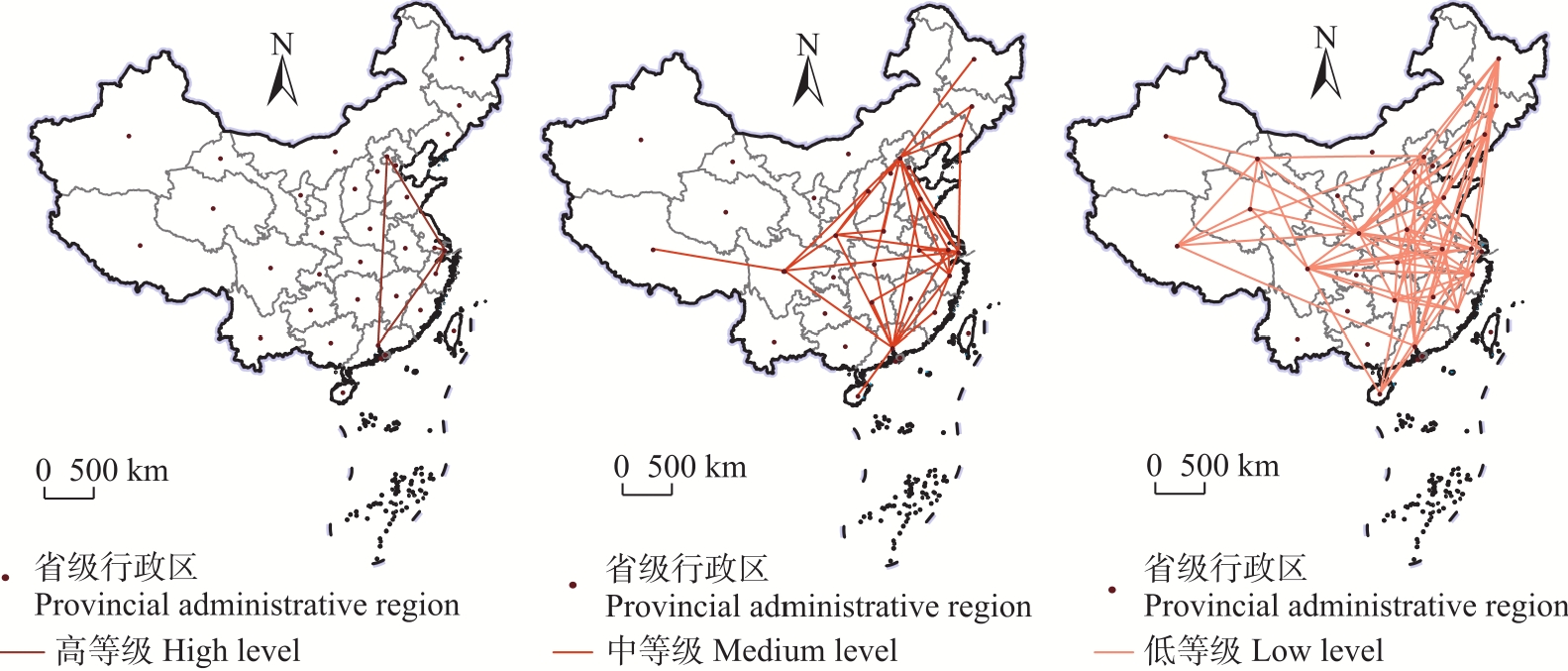
图3 省际入境旅游流循环强度空间分布 注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2020)4624号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改,下文同
Fig. 3 Spatial distribution of inter-provincial inbound tourism circulation intensity
| 省区市Provinces | 度数中心度Degree centrality | 接近中心度Closeness centrality | 中间中心度Betweenness centrality | 结构洞Structural Holes | 网络规模Network size | 个体网络密度Individual network density | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效规模Effective size | 效率Efficiency | 限制度Constraint | ||||||
| 北京 | 76.000 | 80.645 | 9.633 | 10.200 | 0.510 | 0.193 | 19 | 0.462 0 |
| 天津 | 4.000 | 42.373 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 1.125 | 1 | 0.000 0 |
| 河北 | 16.000 | 51.020 | 0.074 | 1.400 | 0.280 | 0.638 | 4 | 0.833 3 |
| 山西 | 20.000 | 55.556 | 0.074 | 1.333 | 0.222 | 0.555 | 5 | 0.900 0 |
| 辽宁 | 40.000 | 62.500 | 1.160 | 3.545 | 0.322 | 0.327 | 10 | 0.688 9 |
| 吉林 | 20.000 | 54.348 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.167 | 0.560 | 5 | 1.000 0 |
| 黑龙江 | 40.000 | 60.976 | 1.499 | 4.273 | 0.388 | 0.329 | 10 | 0.600 0 |
| 上海 | 60.000 | 71.429 | 11.386 | 7.750 | 0.484 | 0.236 | 15 | 0.485 7 |
| 江苏 | 52.000 | 67.568 | 1.625 | 4.429 | 0.316 | 0.264 | 13 | 0.692 3 |
| 浙江 | 52.000 | 67.568 | 2.823 | 4.714 | 0.337 | 0.263 | 13 | 0.666 7 |
| 安徽 | 32.000 | 59.524 | 0.104 | 1.222 | 0.136 | 0.396 | 8 | 0.964 3 |
| 福建 | 36.000 | 58.140 | 0.316 | 2.200 | 0.220 | 0.358 | 9 | 0.833 3 |
| 江西 | 12.000 | 48.077 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.250 | 0.766 | 3 | 1.000 0 |
| 山东 | 36.000 | 60.976 | 0.412 | 2.400 | 0.240 | 0.358 | 9 | 0.805 6 |
| 河南 | 40.000 | 60.976 | 0.735 | 3.000 | 0.273 | 0.329 | 10 | 0.755 6 |
| 湖北 | 40.000 | 60.976 | 0.485 | 2.818 | 0.256 | 0.328 | 10 | 0.777 8 |
| 湖南 | 36.000 | 60.976 | 1.625 | 3.600 | 0.360 | 0.358 | 9 | 0.638 9 |
| 广东 | 80.000 | 83.333 | 12.245 | 11.000 | 0.524 | 0.185 | 20 | 0.447 4 |
| 海南 | 24.000 | 54.348 | 0.037 | 1.286 | 0.184 | 0.490 | 6 | 0.933 3 |
| 四川 | 64.000 | 73.529 | 6.817 | 7.588 | 0.446 | 0.220 | 16 | 0.533 3 |
| 西藏 | 24.000 | 55.556 | 0.429 | 1.857 | 0.265 | 0.485 | 6 | 0.800 0 |
| 陕西 | 80.000 | 83.333 | 23.859 | 12.048 | 0.574 | 0.183 | 20 | 0.389 5 |
| 甘肃 | 24.000 | 54.348 | 0.994 | 2.429 | 0.347 | 0.480 | 6 | 0.666 7 |
| 青海 | 16.000 | 51.020 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.200 | 0.648 | 4 | 1.000 0 |
| 宁夏 | 4.000 | 46.296 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 1.125 | 1 | 0.000 0 |
| 新疆 | 8.000 | 47.170 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.333 | 0.926 | 2 | 1.000 0 |
表2 入境旅游流循环个体网络结构特征指标
Tab. 2 Inbound tourism flow circulation individual network structure characteristics indicators
| 省区市Provinces | 度数中心度Degree centrality | 接近中心度Closeness centrality | 中间中心度Betweenness centrality | 结构洞Structural Holes | 网络规模Network size | 个体网络密度Individual network density | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效规模Effective size | 效率Efficiency | 限制度Constraint | ||||||
| 北京 | 76.000 | 80.645 | 9.633 | 10.200 | 0.510 | 0.193 | 19 | 0.462 0 |
| 天津 | 4.000 | 42.373 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 1.125 | 1 | 0.000 0 |
| 河北 | 16.000 | 51.020 | 0.074 | 1.400 | 0.280 | 0.638 | 4 | 0.833 3 |
| 山西 | 20.000 | 55.556 | 0.074 | 1.333 | 0.222 | 0.555 | 5 | 0.900 0 |
| 辽宁 | 40.000 | 62.500 | 1.160 | 3.545 | 0.322 | 0.327 | 10 | 0.688 9 |
| 吉林 | 20.000 | 54.348 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.167 | 0.560 | 5 | 1.000 0 |
| 黑龙江 | 40.000 | 60.976 | 1.499 | 4.273 | 0.388 | 0.329 | 10 | 0.600 0 |
| 上海 | 60.000 | 71.429 | 11.386 | 7.750 | 0.484 | 0.236 | 15 | 0.485 7 |
| 江苏 | 52.000 | 67.568 | 1.625 | 4.429 | 0.316 | 0.264 | 13 | 0.692 3 |
| 浙江 | 52.000 | 67.568 | 2.823 | 4.714 | 0.337 | 0.263 | 13 | 0.666 7 |
| 安徽 | 32.000 | 59.524 | 0.104 | 1.222 | 0.136 | 0.396 | 8 | 0.964 3 |
| 福建 | 36.000 | 58.140 | 0.316 | 2.200 | 0.220 | 0.358 | 9 | 0.833 3 |
| 江西 | 12.000 | 48.077 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.250 | 0.766 | 3 | 1.000 0 |
| 山东 | 36.000 | 60.976 | 0.412 | 2.400 | 0.240 | 0.358 | 9 | 0.805 6 |
| 河南 | 40.000 | 60.976 | 0.735 | 3.000 | 0.273 | 0.329 | 10 | 0.755 6 |
| 湖北 | 40.000 | 60.976 | 0.485 | 2.818 | 0.256 | 0.328 | 10 | 0.777 8 |
| 湖南 | 36.000 | 60.976 | 1.625 | 3.600 | 0.360 | 0.358 | 9 | 0.638 9 |
| 广东 | 80.000 | 83.333 | 12.245 | 11.000 | 0.524 | 0.185 | 20 | 0.447 4 |
| 海南 | 24.000 | 54.348 | 0.037 | 1.286 | 0.184 | 0.490 | 6 | 0.933 3 |
| 四川 | 64.000 | 73.529 | 6.817 | 7.588 | 0.446 | 0.220 | 16 | 0.533 3 |
| 西藏 | 24.000 | 55.556 | 0.429 | 1.857 | 0.265 | 0.485 | 6 | 0.800 0 |
| 陕西 | 80.000 | 83.333 | 23.859 | 12.048 | 0.574 | 0.183 | 20 | 0.389 5 |
| 甘肃 | 24.000 | 54.348 | 0.994 | 2.429 | 0.347 | 0.480 | 6 | 0.666 7 |
| 青海 | 16.000 | 51.020 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.200 | 0.648 | 4 | 1.000 0 |
| 宁夏 | 4.000 | 46.296 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 1.125 | 1 | 0.000 0 |
| 新疆 | 8.000 | 47.170 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.333 | 0.926 | 2 | 1.000 0 |
| 循环板块Cycle plate | 板块一接收关系数Reception count for Plate One | 板块二接收关系数Reception count for Plate Two | 板块三接收关系数Reception count for Plate Three | 板块四接收关系数Reception count for Plate Four | 板块成员总数Total plate members | 实际内部关系比例Actual internal relation ratio | 期望内部关系比例Expected internal relationratio | 接受板块外关系数External relation admission count | 板块类型Plate type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 板块一 | 40 | 28 | 18 | 11 | 8 | 41.24% | 28.00% | 57 | 主受益 |
| 板块二 | 28 | 22 | 5 | 14 | 6 | 31.88% | 20.00% | 47 | 主受益 |
| 板块三 | 18 | 5 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 20.00% | 29 | 主溢出 |
| 板块四 | 11 | 14 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 20.51% | 20.00% | 31 | 主受益 |
表3 入境旅游流循环网络的板块特征
Tab. 3 Plate characteristics of the inbound tourism flow circulation network
| 循环板块Cycle plate | 板块一接收关系数Reception count for Plate One | 板块二接收关系数Reception count for Plate Two | 板块三接收关系数Reception count for Plate Three | 板块四接收关系数Reception count for Plate Four | 板块成员总数Total plate members | 实际内部关系比例Actual internal relation ratio | 期望内部关系比例Expected internal relationratio | 接受板块外关系数External relation admission count | 板块类型Plate type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 板块一 | 40 | 28 | 18 | 11 | 8 | 41.24% | 28.00% | 57 | 主受益 |
| 板块二 | 28 | 22 | 5 | 14 | 6 | 31.88% | 20.00% | 47 | 主受益 |
| 板块三 | 18 | 5 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 20.00% | 29 | 主溢出 |
| 板块四 | 11 | 14 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 20.51% | 20.00% | 31 | 主受益 |
| 板块一 Plate One | 板块二 Plate Two | 板块三 Plate Three | 板块四 Plate Four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 板块一 | 0.714 | 0.583 | 0.375 | 0.229 |
| 板块二 | 0.583 | 0.733 | 0.139 | 0.389 |
| 板块三 | 0.375 | 0.139 | 0.000 | 0.167 |
| 板块四 | 0.229 | 0.389 | 0.167 | 0.267 |
表4 各入境旅游流循环板块的密度矩阵
Tab. 4 Density matrix of each inbound tourism flow circulation plate
| 板块一 Plate One | 板块二 Plate Two | 板块三 Plate Three | 板块四 Plate Four | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 板块一 | 0.714 | 0.583 | 0.375 | 0.229 |
| 板块二 | 0.583 | 0.733 | 0.139 | 0.389 |
| 板块三 | 0.375 | 0.139 | 0.000 | 0.167 |
| 板块四 | 0.229 | 0.389 | 0.167 | 0.267 |
| 核心区Core zone | 半边缘区Semi-Peripheral zone | 边缘区Peripheral zone |
|---|---|---|
| 北京、上海、江苏、浙江、河南、湖北、广东、四川、陕西 | 山西、辽宁、吉林、黑龙江、安徽、福建、山东、湖南、海南、西藏 | 天津、河北、江西、甘肃、青海、宁夏、新疆 |
表5 入境旅游流循环网络的核心—边缘省区市
Tab. 5 Core-Peripheral provinces of the inbound tourism flow circulation network
| 核心区Core zone | 半边缘区Semi-Peripheral zone | 边缘区Peripheral zone |
|---|---|---|
| 北京、上海、江苏、浙江、河南、湖北、广东、四川、陕西 | 山西、辽宁、吉林、黑龙江、安徽、福建、山东、湖南、海南、西藏 | 天津、河北、江西、甘肃、青海、宁夏、新疆 |
| 自变量Independent variable | 非标准化回归系数Unstandardized regression coefficient | 标准化回归系数Standardized regression coefficient | 显著性概率Significance probability | 概率1Probability 1 | 概率2Probability 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 截距 | 0.002 0 | 0.000 0 | |||
| 交通便捷程度矩阵 | -0.167 9 | -0.247 7 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
| 对外经济贸易矩阵 | 0.172 1 | 0.288 0 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 |
| 旅游资源禀赋矩阵 | -0.089 7 | -0.215 6 | 0.031 | 0.969 | 0.031 |
| 经济发展水平矩阵 | 0.395 7 | 0.731 7 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 旅游接待能力矩阵 | 0.004 5 | 0.010 1 | 0.470 | 0.470 | 0.530 |
| R2 | 0.509 |
表6 入境旅游流循环强度影响因素矩阵的QAP回归结果
Tab. 6 QAP regression results of the matrix of factors influencing the inbound tourism flow circulation intensity
| 自变量Independent variable | 非标准化回归系数Unstandardized regression coefficient | 标准化回归系数Standardized regression coefficient | 显著性概率Significance probability | 概率1Probability 1 | 概率2Probability 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 截距 | 0.002 0 | 0.000 0 | |||
| 交通便捷程度矩阵 | -0.167 9 | -0.247 7 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
| 对外经济贸易矩阵 | 0.172 1 | 0.288 0 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.000 |
| 旅游资源禀赋矩阵 | -0.089 7 | -0.215 6 | 0.031 | 0.969 | 0.031 |
| 经济发展水平矩阵 | 0.395 7 | 0.731 7 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 旅游接待能力矩阵 | 0.004 5 | 0.010 1 | 0.470 | 0.470 | 0.530 |
| R2 | 0.509 |
| 自变量Independent variable | 非标准化回归系数 Unstandardized regression coefficient | 标准化回归系数 Standardized regression coefficient | 显著性概率 Significance probability | 概率1 Probability 1 | 概率2 Probability 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 截距 | 0.008 3 | 0.000 0 | - | - | - |
| 交通便捷程度矩阵 | 0.439 7 | 0.300 0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 对外经济贸易匹配矩阵 | -0.118 5 | -0.107 5 | 0.028 | 0.972 | 0.028 |
| 旅游资源禀赋匹配矩阵 | 0.066 6 | 0.081 3 | 0.150 | 0.150 | 0.850 |
| 经济发展水平匹配矩阵 | 0.256 4 | 0.300 6 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 旅游接待能力匹配矩阵 | 0.189 6 | 0.228 7 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.993 |
| R2 | 0.541 | - | - | - | - |
表7 入境旅游流循环流量规模匹配度影响因素矩阵的QAP回归结果
Tab. 7 QAP regression results of the matrix of factors influencing the matching degree of flow scale of inbound tourism flow circulation
| 自变量Independent variable | 非标准化回归系数 Unstandardized regression coefficient | 标准化回归系数 Standardized regression coefficient | 显著性概率 Significance probability | 概率1 Probability 1 | 概率2 Probability 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 截距 | 0.008 3 | 0.000 0 | - | - | - |
| 交通便捷程度矩阵 | 0.439 7 | 0.300 0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 对外经济贸易匹配矩阵 | -0.118 5 | -0.107 5 | 0.028 | 0.972 | 0.028 |
| 旅游资源禀赋匹配矩阵 | 0.066 6 | 0.081 3 | 0.150 | 0.150 | 0.850 |
| 经济发展水平匹配矩阵 | 0.256 4 | 0.300 6 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 旅游接待能力匹配矩阵 | 0.189 6 | 0.228 7 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.993 |
| R2 | 0.541 | - | - | - | - |
| 自变量Independent variable | 非标准化回归系数 Unstandardized regression coefficient | 标准化回归系数Standardized regression coefficient | 显著性概率Significance probability | 概率1Probability 1 | 概率2Probability2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 截距 | -0.000 7 | 0.000 0 | - | - | - |
| 交通便捷程度矩阵 | 0.105 3 | 0.079 6 | 0.080 | 0.080 | 0.921 |
| 对外经济贸易匹配矩阵 | -0.020 0 | -0.020 1 | 0.370 | 0.630 | 0.370 |
| 旅游资源禀赋匹配矩阵 | 0.115 8 | 0.156 6 | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.968 |
| 经济发展水平匹配矩阵 | 0.353 7 | 0.459 5 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 旅游接待能力匹配矩阵 | 0.042 0 | 0.056 2 | 0.252 | 0.252 | 0.748 |
| R2 | 0.460 | - | - | - | - |
表8 入境旅游流循环流向偏好匹配度影响因素矩阵的QAP回归结果
Tab. 8 QAP regression results of the matrix of factors influencing the matching degree of flow preference of inbound tourism flow circulation
| 自变量Independent variable | 非标准化回归系数 Unstandardized regression coefficient | 标准化回归系数Standardized regression coefficient | 显著性概率Significance probability | 概率1Probability 1 | 概率2Probability2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 截距 | -0.000 7 | 0.000 0 | - | - | - |
| 交通便捷程度矩阵 | 0.105 3 | 0.079 6 | 0.080 | 0.080 | 0.921 |
| 对外经济贸易匹配矩阵 | -0.020 0 | -0.020 1 | 0.370 | 0.630 | 0.370 |
| 旅游资源禀赋匹配矩阵 | 0.115 8 | 0.156 6 | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.968 |
| 经济发展水平匹配矩阵 | 0.353 7 | 0.459 5 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| 旅游接待能力匹配矩阵 | 0.042 0 | 0.056 2 | 0.252 | 0.252 | 0.748 |
| R2 | 0.460 | - | - | - | - |
| [1] | Barnett G A. Encyclopedia of Social Networks[M]. Los Angeles: SAGE Publications, 2011. |
| [2] | Huang H P, Zhong W, Lai Q S, et al. The spatial distribution, influencing factors, and development path of inbound tourism in China—An empirical analysis of market segments based on travel motivation[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(6): 2508. |
| [3] | Liu J J, Nijkamp P. Inbound tourism as a driving force for regional innovation: A spatial impact study on China[J]. Journal of Travel Research, 2019, 58(4): 594-607. |
| [4] | Liu Y P, Li Y C, Parkpian P. Inbound tourism in Thailand: Market form and scale differentiation in ASEAN source countries[J]. Tourism Management, 2018(64): 22-36. |
| [5] | Mou N X, Yuan R Z, Yang T F, et al. Exploring spatio-temporal changes of city inbound tourism flow: The case of Shanghai, China[J]. Tourism Management, 2020(76): 103955. |
| [6] | Silva E S, Hassani H. ‘Modelling’UK tourism demand using fashion retail sales[J]. Annals of Tourism Research, 2022(95): 103428. |
| [7] | Zeng B D. Pattern of Chinese tourist flows in Japan: A Social Network Analysis perspective[J]. Tourism Geographies, 2018, 20(5): 810-832. |
| [8] | Zhang H W, Jiang Z Y, Gao W, et al. Time-varying impact of economic policy uncertainty and geopolitical risk on tourist arrivals: Evidence from a developing country[J]. Tourism Management Perspectives, 2022(41): 100928. |
| [9] | Zhu H. Multilevel understanding dynamic changes in inbound tourist flow network (ITFN) structure: Topology, collaboration, and competitiveness[J]. Current Issues in Tourism, 2021, 24(14): 2059-2077. |
| [10] | 段志勇, 汪侠, 刘丹丽, 等. 国内外旅游交通研究现状及展望[J]. 旅游导刊, 2018, 2(4): 70-89. |
| [DUAN Zhiyong, WANG Xia, LIU Danli, et al. Review and prospect of tourism transportation research[J]. Tourism and Hospitality Prospects, 2018, 2(4): 70-89.] | |
| [11] | 雷可为, 陈瑛. 基于BP神经网络和ARIMA组合模型的中国入境游客量预测[J]. 旅游学刊, 2007, 22(4): 20-25. |
| [LEI Kewei, CHEN Ying. Forecast of inbound tourists to China based on BP neural network and ARIMA combined model[J]. Tourism Tribune, 2007, 22(4): 20-25.] | |
| [12] | 李创新, 马耀峰, 张颖, 等. 时空二元视角的入境旅游流集散空间场效应与地域结构——以丝路东段典型区为例[J]. 地理科学, 2012, 32(2): 176-185. |
| [LI Chuangxin, MA Yaofeng, ZHANG Ying, et al. The spatial field effect and regional structure of concentration and diffusion of inbound tourism flows on spatial and temporal scale: Case of typical district of the eastern part of the silk road[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2012, 32(2): 176-185.] | |
| [13] | 李磊, 陶卓民, 陆林, 等. 贵州省避暑旅游流网络结构特征及其影响因素[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(11): 3208-3224. |
| [LI Lei, TAO Zhuomin, LU Lin, et al. Structural characteristics and influencing factors of summer tourism flow network in Guizhou province[J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(11): 3208-3224.] | |
| [14] | 李善同, 侯永志. 中国大陆:划分8大社会经济区域[J]. 经济前沿, 2003(5): 12-15. |
| [LI shantung, HOU yongzhi. Chinese Mainland: divided into 8 socio-economic regions[J]. Forward Position in Economics, 2003(5): 12-15.] | |
| [15] | 梁逍遥, 马丽君. 我国国内旅游流循环空间格局及形成机理——基于网络关注度的分析[J]. 旅游学刊, 2023, 38(9): 104-117. |
| [LIANG Xiaoyao, MA Lijun. The spatial pattern and formation mechanism of domestic tourist flow circulations—Analysis based on network attention data[J]. Tourism Tribune, 2023, 38(9): 104-117.] | |
| [16] | 刘法建, 张捷, 陈冬冬. 中国入境旅游流网络结构特征及动因研究[J]. 地理学报, 2010, 65(8): 1013-1024. |
| [LIU Fajian, ZHANG Jie, CHEN Dongdong. The characteristics and dynamical factors of Chinese inbound tourist flow network[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2010, 65(8): 1013-1024.] | |
| [17] | 卢淑莹, 陶卓民, 李涛, 等. 泛长三角区域入境游客空间格局与意象研究[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(1): 263-278. |
| [LU Shuying, TAO Zhuomin, LI Tao, et al. Study on the spatial pattern and image of inbound tourists in the Pan-Yangtze River Delta[J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(1): 263-278.] | |
| [18] | 马丽君, 邓思凡. 省际入境与国内旅游流网络结构特征及比较分析[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2021, 37(5): 133-142. |
| [MA Lijun, DENG Sifan. Characteristics and comparative analysis of inter-provincial inbound and domestic tourist flow network structure[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2021, 37(5): 133-142.] | |
| [19] | 马丽君, 孙根年, 黄芸玛, 等. 城市国内客流量与游客网络关注度时空相关分析[J]. 经济地理, 2011, 31(4): 680-685. |
| [MA Lijun, SUN Gennian, HUANG Yunma, et al. A correlative analysis on the relationship between domestic tourists and network attention[J]. Economic Geography, 2011, 31(4): 680-685.] | |
| [20] | 秦静, 李郎平, 唐鸣镝, 等. 基于地理标记照片的北京市入境旅游流空间特征[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(8): 1556-1570. |
| [QIN Jing, LI Langping, TANG Mingdi, et al. Exploring the spatial characteristics of Beijing inbound tourist flow based on geotagged photos[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(8): 1556-1570.] | |
| [21] | 任君, 黄明理. “双循环”新发展格局研究述评[J]. 经济问题, 2021(4): 7-15. |
| [REN Jun, HUANG Mingli. A summary of studies on “double cycle” new development pattern[J]. On Economic Problems, 2021(4): 7-15.] | |
| [22] | 荣晨, 盛朝迅, 易宇, 等. 国内大循环的突出堵点和应对举措研究[J]. 宏观经济研究, 2021(1): 5-18, 78. |
| [RONG Chen, SHENG Chaoxun, YI Yu, et al. A study on outstanding blocking points and countermeasures of the domestic grand cycle[J]. Macroeconomics, 2021(1): 5-18, 78.] | |
| [23] | 沈丽珍, 陈少杰, 汪侠. 流动空间视角下的同城化地区发展阶段划分与特征[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(9): 2558-2571. |
| [SHEN Lizhen, CHEN Shaojie, WANG Xia. Development stage segmentation and characteristics of urban integration area in China based on the space of flows[J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(9): 2558-2571.] | |
| [24] | 沈苏彦, 赵锦, 徐坚. 基于“谷歌趋势”数据的入境外国游客量预测[J]. 资源科学, 2015, 37(11): 2111-2119. |
| [SHEN Suyan, ZHAO Jin, XU Jian. Forecasting China inbound tourism with Google trend data[J]. Resources Science, 2015, 37(11): 2111-2119.] | |
| [25] | 孙根年, 周功梅, 李红. 中美入境旅游, 谁的市场更大——基于多样性、重要性、旅游偏好及市场吨位的比较[J]. 旅游科学, 2015, 29(3): 15-26. |
| [SUN Gennian, ZHOU Gongmei, LI Hong. A comparison of inbound tourism in China and U.S: Based on market diversity, proportion of international outbound trips, travel preference and travel tonnage index[J]. Tourism Science, 2015, 29(3): 15-26.] | |
| [26] | 唐顺铁, 郭来喜. 旅游流体系研究[J]. 旅游学刊, 1998(3): 38-41. |
| [TANG Shuntie, GUO Laixi. Tourism flow system research[J]. Tourism Tribune, 1998(3): 38-41.] | |
| [27] | 王朝辉, 乔浩浩, 张姗姗, 等. 入境旅游流空间格局演化及大都市旅游高质量发展——以上海市为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(12): 3167-3182. |
| [WANG Chaohui, QIAO Haohao, ZHANG Shanshan, et al. Evolution of spatial pattern of inbound tourism flows and enlightenment of high-quality development of metropolitan tourism: A case stady of Shanghai[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2022, 37(12): 3167-3182.] | |
| [28] | 王钦安, 孙根年, 顾梦雅. 安徽省入境旅游流量与流质发展变化分析[J]. 华东经济管理, 2016, 30(3): 27-33. |
| [WANG Qinan, SUN Gennian, GU Mengya. An analysis on the changes of quantity and quality of inbound tourism flow to Anhui province[J]. East China Economic Management, 2016, 30(3): 27-33.] | |
| [29] | 王永明, 王美霞, 吴殿廷, 等. 基于ZINB模型的中国省域间入境旅游流影响因素[J]. 经济地理, 2018, 38(11): 234-240. |
| [WANG Yongming, WANG Meixia, WU Dianting, et al. Determinants of inbound tourism flows between provinces in China based on ZINB model[J]. Economic Geography, 2018, 38(11): 234-240.] | |
| [30] | 王钊, 李涛. 中国入境旅游流集散优势度与旅游经济效率的时空耦合分析[J]. 人文地理, 2021, 36(5): 157-166. |
| [WANG Zhao, LI Tao. Spatiotemporal coupling analysis of China’s inbound tourism distributive superiority and tourism economic efficiency[J]. Human Geography, 2021, 36(5): 157-166.] | |
| [31] | 薛华菊, 马耀峰, 黄毅, 等. 区域入境旅游流质量时空演变及特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(6): 171-176. |
| [XUE Huaju, MA Yaofeng, HUANG Yi, et al. Study on spatiotemporal evolution and characters of Chinese regional inbound tourism flow quality[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(6): 171-176.] | |
| [32] | 姚云霞, 管卫华, 李在军. 江苏省入境旅游流的时空演变及影响因素分析[J]. 旅游科学, 2016, 30(5): 52-62. |
| [YAO Yunxia, GUAN Weihua, LI Zaijun. An analysis of the temporal-spatial evolution of inbound tourist flow of Jiangsu province and its influencing factors[J]. Tourism Science, 2016, 30(5): 52-62.] | |
| [33] | 约瑟夫·熊彼特. 经济发展理论[M]. 郭武军, 吕阳, 译. 北京: 华夏出版社, 2015. |
| [Schumpeter J A. Theory of Economic Development[M]. UO Wujun, LYU Yang, trans. Beijing: Huaxia Publishing House, 2015.] | |
| [34] | 张爱平, 钟林生, 徐勇, 等. 中国省际旅游发展质量特征及空间差异[J]. 地理科学, 2015, 35(3): 283-292. |
| [ZHANG Aiping, ZHONG Linsheng, XU Yong, et al. Characteristics and spatial difference of provincial tourism development quality in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2015, 35(3): 283-292.] | |
| [35] | 张勇, 王珊娜. 畅通国内大循环的分析逻辑与实施脉络[J]. 当代经济管理, 2022, 44(10): 23-28. |
| [ZHANG Yong, WANG Shanna. The promotion of the domestic circulation of China: Analytic logic and realization path[J]. Contemporary Economic Management, 2022, 44(10): 23-28.] | |
| [36] | 张佑印, 马耀峰, 马红丽, 等. 北京入境集聚扩散旅游流平衡点转移规律研究[J]. 旅游学刊, 2009, 24(12): 31-35. |
| [ZHANG Youyin, MA Yaofeng, MA Hongli, et al. Study on the dynamic shift of Beijing convergence-diffusion tourism flow equilibrium point[J]. Tourism Tribune, 2009, 24(12): 31-35.] | |
| [37] | 张占斌. 国内大循环[M]. 长沙: 湖南人民出版社, 2020. |
| [ZHANG Zhanbin. Domestic Macro-Circulation[M]. Changsha: Hunan People’s Publishing House, 2020.] | |
| [38] | 张子昂, 保继刚. 多重距离对中国入境与出境旅游流的影响: 基于组态的视角[J]. 地理科学, 2021, 41(1): 13-21. |
| [ZHANG Ziang, BAO Jigang. Effects of multiple distances on inbound and outbound tourism flows in China: A configuration-based perspective[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2021, 41(1): 13-21.] | |
| [39] | 朱奇. 生产过程论[M]. 西安: 陕西人民出版社, 2011. |
| [ZHU Qi. Theory of Production Process[M]. Xi’an: Shaanxi People’s Publishing House, 2011.] |
| [1] | 陆林, 陈劼绮, 毕珊珊, 许艳, 崔静, 方叶兵. 徽州村落旅游者乡愁感知及其影响因素研究[J]. 旅游导刊, 2023, 7(6): 59-76. |
| [2] | 孙媛媛, 时少华. 基于网络游记的运河沿岸城市旅游流网络结构特征及影响因素研究[J]. 旅游导刊, 2023, 7(5): 43-65. |
| [3] | 周波,肖洪根,叶顺. 国外旅游领域中的知识转移研究:述评与展望[J]. 旅游导刊, 2021, 5(5): 87-106. |
| [4] | 宋昌耀, 贾然, 厉新建. 过境免签政策与入境旅游增长——基于PSM-DID方法的分析[J]. 旅游导刊, 2018, 2(6): 33-46. |
| [5] | 吴艺娟, 郑向敏. 旅游者安全行为外文研究文献综述[J]. 旅游导刊, 2017, 1(5): 68-85. |
| [6] | 邹永广, 林炜铃. “驴友”安全事故影响因素重要度评价研究[J]. 旅游导刊, 2017, 1(4): 57-70. |
| [7] | 唐健雄, 孙桥. 新常态下委托管理饭店知识转移的影响因素研究[J]. 旅游导刊, 2017, 1(2): 60-78. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||