

微信公众号

编辑部微信号
旅游导刊 ›› 2023, Vol. 7 ›› Issue (5): 43-65.DOI: 10.12054/lydk.bisu.236
收稿日期:2023-03-28
修回日期:2023-08-28
出版日期:2023-10-30
发布日期:2023-11-07
通讯作者:
时少华(1978— ),男,山东日照人,博士,北京联合大学旅游学院教授,研究方向:旅游管理、文化遗产管理研究。E-mail:shishaohua978222@163.com作者简介:孙媛媛(1999— ),女,安徽合肥人,北京联合大学旅游学院硕士研究生,研究方向:旅游管理。
基金资助:Received:2023-03-28
Revised:2023-08-28
Online:2023-10-30
Published:2023-11-07
摘要:
运河沿岸城市旅游流网络结构特征及影响因素研究对运河旅游发展具有重要意义,本文从39个运河沿岸城市的旅游者网络游记中提取流动信息构建旅游流网络,运用社会网络分析法(SNA)和指数随机图模型(ERGM)分析旅游流网络结构特征及不同因素对运河沿岸城市旅游流网络的共同影响。通过探究运河沿岸城市旅游流网络结构特征的深层影响机理,发现旅游流网络结构特征是多种因素共同作用的结果:(1)旅游吸引力导致长三角地区运河沿岸城市旅游流频数分布呈现差异性;(2)旅游流集散能力受经济发展水平、城市可达性、城市环境质量和城市旅游吸引力共同影响;(3)核心中转城市的非替代性主要源于城市高可达性;(4)经济发展水平是核心—边缘结构特征形成的重要影响因素。本文对运河沿岸城市旅游流规划管理与可持续发展具有启示意义。
中图分类号:
孙媛媛, 时少华. 基于网络游记的运河沿岸城市旅游流网络结构特征及影响因素研究[J]. 旅游导刊, 2023, 7(5): 43-65.
SUN Yuanyuan, SHI Shaohua. Research on the Structural Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Urban Tourism Flow Networks along the Grand Canals: Insights from Online Travelogues[J]. Tourism and Hospitality Prospects, 2023, 7(5): 43-65.
| 区域 Area | 名称 Name |
|---|---|
| 直辖市 | 北京、天津 |
| 河北省 | 沧州、廊坊、保定、衡水、邢台、邯郸 |
| 山东省 | 德州、泰安、聊城、济宁、枣庄 |
| 河南省 | 洛阳、郑州、开封、商丘、焦作、新乡、鹤壁、安阳、濮阳 |
| 安徽省 | 淮北、宿州、宣城 |
| 江苏省 | 宿迁、徐州、淮安、扬州、镇江、常州、无锡、苏州、泰州 |
| 浙江省 | 嘉兴、杭州、湖州、绍兴、宁波 |
表1 运河沿岸城市分布
Tab.1 Distribution of cities along the canal
| 区域 Area | 名称 Name |
|---|---|
| 直辖市 | 北京、天津 |
| 河北省 | 沧州、廊坊、保定、衡水、邢台、邯郸 |
| 山东省 | 德州、泰安、聊城、济宁、枣庄 |
| 河南省 | 洛阳、郑州、开封、商丘、焦作、新乡、鹤壁、安阳、濮阳 |
| 安徽省 | 淮北、宿州、宣城 |
| 江苏省 | 宿迁、徐州、淮安、扬州、镇江、常州、无锡、苏州、泰州 |
| 浙江省 | 嘉兴、杭州、湖州、绍兴、宁波 |
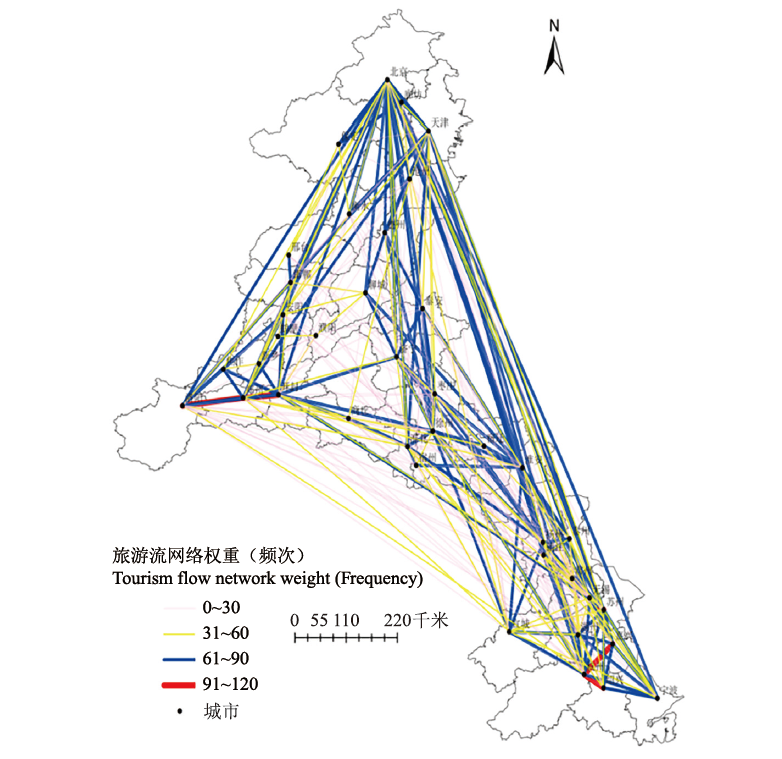
图1 运河沿岸城市旅游流网络结构 注:本图根据自然资源部监制的标准地图[审图号GS(2023)336号]制作,底图无修改;此图仅作示意,如需清晰大图,请与编辑部联系,图2同
Fig. 1 The network structure of tourism flow in cities along the canal
| 一级指标 First-level indicator | 二级指标 Second-level indicator | 二级指标构成 Second-level indicator composition | 预期影响 Expected impact | 文献依据 Literature source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城市旅游 吸引力 Urban tourism attraction | 网络 关注度 NA (万次/年) | 选取2017年至2019年关键词“城市名”“城市名+运河”“城市名+运河+旅游”的日均百度指数,汇总后得到每个城市年均运河网络关注度 | + | 汪秋菊、黄明、刘宇, |
| 运河旅游 资源禀赋 ATR | D为旅游资源禀赋,Q为城市内A级以上运河旅游景点个数,W为权重(AAAAA级景点加权5分,AAAA级景点加权4分,以此类推),S为面积(km2),P为年平均人口(万人) | + | 王永明、王美霞、吴殿廷等, | |
| 城市环境 质量 Urban environmental quality | 建成区 绿化率 GR (‰) | 据《中国城市统计年鉴》,取2017年至2019年建成区绿化率平均值 | + | 刘庆芳、王兆峰, |
| 空气质量 指数AQI | 按照美国环境保护署公布的PM2.5年均浓度和空气质量之间的划分标准,将处于15.5~150.4(μg/m3)区间内的细颗粒物(PM2.5)年均浓度划分为空气质量较好、中等、较差3个等级 | + | 杜家禛、徐菁、靳诚, | |
| 城市 可达性 Urban accessibility | 加权平均 旅行时间 CR (小时) | 考虑到现代游客的出行习惯,时间距离更能反映交通的便捷程度,计算公式为: 其中,Ai为节点城市i的可达性,Tij为借助交通工具从节点城市i到达节点城市j所花费的最短时间(小时),Mj为节点j的城市质量(即权重),1≤j≤39,j=1即为北京,依此类推,GDP为地区生产总值(亿元),POUP为城市人口数(千万人) | - | 马丽君、肖洋, |
| 空间 邻近性 CP | 根据城市行政区划图,若两地相邻,则赋值为1,否则赋值为0,是空间邻接关系数据、二元网络属性变量 | + | 杜家禛、徐菁、靳诚, | |
| 经济发展 水平 Level of economic development | 城市 生产总值 GDP (亿元) | 据《中国城市统计年鉴》,各城市分别取其2017年至2019年3年城市生产总值的平均值 | + | 马丽君、肖洋, |
| 人均 生产总值 PGDP (元) | 据《中国城市统计年鉴》,各城市分别取其2017年至2019年3年人均生产总值的平均值 | + | Yang,Han & Gong,et al., |
表2 运河沿岸城市旅游流网络的影响因素指标
Tab.2 Indicators of influencing factors of tourism flow network in cities along the canal
| 一级指标 First-level indicator | 二级指标 Second-level indicator | 二级指标构成 Second-level indicator composition | 预期影响 Expected impact | 文献依据 Literature source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城市旅游 吸引力 Urban tourism attraction | 网络 关注度 NA (万次/年) | 选取2017年至2019年关键词“城市名”“城市名+运河”“城市名+运河+旅游”的日均百度指数,汇总后得到每个城市年均运河网络关注度 | + | 汪秋菊、黄明、刘宇, |
| 运河旅游 资源禀赋 ATR | D为旅游资源禀赋,Q为城市内A级以上运河旅游景点个数,W为权重(AAAAA级景点加权5分,AAAA级景点加权4分,以此类推),S为面积(km2),P为年平均人口(万人) | + | 王永明、王美霞、吴殿廷等, | |
| 城市环境 质量 Urban environmental quality | 建成区 绿化率 GR (‰) | 据《中国城市统计年鉴》,取2017年至2019年建成区绿化率平均值 | + | 刘庆芳、王兆峰, |
| 空气质量 指数AQI | 按照美国环境保护署公布的PM2.5年均浓度和空气质量之间的划分标准,将处于15.5~150.4(μg/m3)区间内的细颗粒物(PM2.5)年均浓度划分为空气质量较好、中等、较差3个等级 | + | 杜家禛、徐菁、靳诚, | |
| 城市 可达性 Urban accessibility | 加权平均 旅行时间 CR (小时) | 考虑到现代游客的出行习惯,时间距离更能反映交通的便捷程度,计算公式为: 其中,Ai为节点城市i的可达性,Tij为借助交通工具从节点城市i到达节点城市j所花费的最短时间(小时),Mj为节点j的城市质量(即权重),1≤j≤39,j=1即为北京,依此类推,GDP为地区生产总值(亿元),POUP为城市人口数(千万人) | - | 马丽君、肖洋, |
| 空间 邻近性 CP | 根据城市行政区划图,若两地相邻,则赋值为1,否则赋值为0,是空间邻接关系数据、二元网络属性变量 | + | 杜家禛、徐菁、靳诚, | |
| 经济发展 水平 Level of economic development | 城市 生产总值 GDP (亿元) | 据《中国城市统计年鉴》,各城市分别取其2017年至2019年3年城市生产总值的平均值 | + | 马丽君、肖洋, |
| 人均 生产总值 PGDP (元) | 据《中国城市统计年鉴》,各城市分别取其2017年至2019年3年人均生产总值的平均值 | + | Yang,Han & Gong,et al., |
| 参数估计量 Parameter estimator | 估计值 Estimated value | 标准误 Standard error | t-比率 t-ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| NA网络关注度 | 0.455 391* | 0.113 41 | 0.041 |
| ATR运河旅游资源禀赋 | -0.327 117 | 0.245 78 | 0.027 |
| GR建成区绿化率 | 1.284 967* | 0.113 51 | 0.081 |
| AQI空气质量指数 | -0.367 079 | 0.096 76 | -0.020 |
| CR加权平均旅行时间 | -1.151 080* | 0.106 54 | -0.019 |
| CP空间邻近性 | 0.599 393* | 0.194 42 | 0.004 |
| GDP城市生产总值 | 2.016 749* | 0.424 21 | 0.087 |
| PGDP人均生产总值 | 2.002 543* | 0.137 89 | 0.071 |
表3 模型参数估计及拟合优度检验
Tab. 3 Model parameter estimation and test goodness of fit
| 参数估计量 Parameter estimator | 估计值 Estimated value | 标准误 Standard error | t-比率 t-ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| NA网络关注度 | 0.455 391* | 0.113 41 | 0.041 |
| ATR运河旅游资源禀赋 | -0.327 117 | 0.245 78 | 0.027 |
| GR建成区绿化率 | 1.284 967* | 0.113 51 | 0.081 |
| AQI空气质量指数 | -0.367 079 | 0.096 76 | -0.020 |
| CR加权平均旅行时间 | -1.151 080* | 0.106 54 | -0.019 |
| CP空间邻近性 | 0.599 393* | 0.194 42 | 0.004 |
| GDP城市生产总值 | 2.016 749* | 0.424 21 | 0.087 |
| PGDP人均生产总值 | 2.002 543* | 0.137 89 | 0.071 |
| [1] | Frank O, Strauss D. Markov graphs[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1986, 81(395):832-842. |
| [2] | Friedmann J. Regional Development Policy:A Case Study of Venezuela[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press,1966. |
| [3] | Hatak I, Lang R, Roessl D. Trust,social capital,and the coordination of relationships between the members of cooperatives:A comparison between member-focused cooperatives and third-party-focused cooperatives[J]. VOLUNTAS:International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations, 2016, 27(3):1218-1241. |
| [4] | He Y H, Wu L. Analysis on spatial development mode of eco-sports tourism in Grand Canal landscape environment culture belt[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2022, 194(12):925. |
| [5] | Khan N U, Wan W G, Yu S. Spatiotemporal analysis of tourists and residents in Shanghai based on location-based social network’s data from Weibo[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2020, 9(2):70. |
| [6] | Lojo A, Li M M, Xu H G. Online tourism destination image:Components,information sources,and incongruence[J]. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 2020, 37(4):495-509. |
| [7] | Manoharan S, Ammayappan S. Geospatial and social media analytics for emotion analysis of theme park visitors using text mining and GIS[J]. Journal of Information Technology and Digital World, 2020, 2(2):100-107. |
| [8] | Mou N X, Zheng Y H, Makkon T, et al. Tourists’ digital footprint:The spatial patterns of tourist flows in Qingdao,China[J]. Tourism Management, 2020(81):104151. |
| [9] | Popescu A, Hontus A C, Caratus-Stanciu M. Trends and changes in tourist flow in Romania in the period 2009—2018[J]. Scientific Papers:Management,Economic Engineering in Agriculture & Rural Development, 2020, 20(1):425-436. |
| [10] | Qian Z. World Heritage Site inscription and waterfront heritage conservation:Evidence from the Grand Canal historic districts in Hangzhou,China[J]. Journal of Heritage Tourism, 2021, 16(6):684-704. |
| [11] | Robins G, Snijders T, Wang P, et al. Recent developments in exponential random graph(p*) models for social networks[J]. Social Networks, 2007, 29(2):192-215. |
| [12] | Saluveer E, Raun J, Tiru M, et al. Methodological framework for producing national tourism statistics from mobile positioning data[J]. Annals of Tourism Research, 2020(81):102895. |
| [13] | Snijders T A B, Pattison P E, Robins G L, et al. New specifications for exponential random graph models[J]. Sociological Methodology, 2006, 36(1):99-153. |
| [14] | Wang P, Sharpe K, Robins G L, et al. Exponential random graph(p*) models for affiliation networks[J]. Social Networks, 2009, 31(1):12-25. |
| [15] | Wang Y W, Chen H, Wu X Y. Spatial structure characteristics of tourist attraction cooperation networks in the Yangtze River Delta based on tourism flow[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(21):12036. |
| [16] | Williams A V, Zelinsky W. On some patterns in international tourist flows[J]. Economic Geography, 1970, 46(4):549-567. |
| [17] | Xu C S, Cheng L, Su J, et al. Developing regional ecological networks along the grand canal based on an integrated analysis framework[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2021, 12(6):801-813. |
| [18] | Xu Y, Li J Y, Belyi A, et al. Characterizing destination networks through mobility traces of international tourists :A case study using a nationwide mobile positioning dataset[J]. Tourism Management, 2021(82):104195. |
| [19] | Yang G, Han Y, Gong H, et al. Spatial-temporal response patterns of tourist flow under real-time tourist flow diversion scheme[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(8):3478. |
| [20] | Yang Y, Sha C F, Su W C, et al. Research on online destination image of Zhenjiang section of the grand canal based on network content analysis[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(5):2731. |
| [21] | Zhang M K, Lenzer J H Jr. Mismatched canal conservation and the authorized heritage discourse in urban China:A case of the Hangzhou Section of the Grand Canal[J]. International Journal of Heritage Studies, 2020, 26(2):105-119. |
| [22] | Zhang S Y, Liu J M, Pei T, et al. Tourism value assessment of linear cultural heritage:The case of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal in China[J]. Current Issues in Tourism, 2023, 26(1):47-69. |
| [23] | Zheng Y H, Mou N X, Zhang L X, et al. Chinese tourists in Nordic countries:An analysis of spatio-temporal behavior using geo-located travel blog data[J]. Computers,Environment and Urban Systems, 2021(85):101561. |
| [24] | 杜家禛, 靳诚, 徐菁, 等. 长江三角洲虚拟旅游流空间格局及其影响因素分析[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2021, 44(2):48-54. |
| [DU Jiazhen, JIN Cheng, XU Jing, et al. The spatial pattern of virtual tourism flow and its influencing factors in Yangtze River Delta[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 44(2):48-54.] | |
| [25] | 杜家禛, 徐菁, 靳诚. 基于百度指数的长江三角洲虚拟旅游流流动特征和影响因素分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2021, 30(2):290-301. |
| [DU Jiazhen, XV Jing, JIN Cheng. Regional virtual tourism flow and its influencing factors based on Baidu index:A case study in Yangtze River Delta[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2021, 30(2):290-301.] | |
| [26] | 方叶林, 黄震方, 李经龙, 等. 中国市域旅游流网络结构空间分异及其效应研究——基于携程旅行网的大数据挖掘[J]. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(1):70-82. |
| [FANG Yelin, HUANG Zhenfang, LI Jinglong, et al. Research on the spatial differentiation and effects of network structure in tourism flow in Chinese cities:Big data mining based on Ctrip[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2022, 37(1):70-82.] | |
| [27] | 方叶林, 苏雪晴, 黄震方, 等. 中国东部沿海五大城市群旅游流网络的结构特征及其韧性评估——基于演化韧性的视角[J]. 经济地理, 2022, 42(2):203-211. |
| [FANG Yelin, SU Xueqing, HUANG Zhenfang, et al. Structural characteristics and resilience evaluation of tourism flow networks in five major urban agglomerations in coastal China:From the perspective of evolutionary resilience[J]. Economic Geography, 2022, 42(2):203-211.] | |
| [28] | 贺小荣, 徐海超, 夏凡. 红色旅游流的空间网络结构及其影响因素——以遵义市为例[J]. 旅游论坛, 2021, 14(6):61-71. |
| [HE Xiaorong, XU Haichao, XIA Fan. The spatial network structure and influencing factors of red tourism flow:A case study of Zunyi City[J]. Tourism Forum, 2021, 14(6):61-71.] | |
| [29] | 焦敏, 路璐, 牛福长, 等. 大运河文化带国家重点文物保护单位分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 经济地理, 2023, 43(3):228-239. |
| [JIAO Min, LU Lu, NIU Fuchang, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of national key cultural relics protection units and their driving factors in the grand canal cultural belt[J]. Economic Geography, 2023, 43(3):228-239.] | |
| [30] | 李磊, 陶卓民, 陆林, 等. 贵州省避暑旅游流网络结构特征及其影响因素[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(11):3208-3224. |
| [LI Lei, TAO Zhuomin, LU Lin, et al. Structural characteristics and influencing factors of summer tourism flow network in Guizhou Province[J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(11):3208-3224.] | |
| [31] | 李倩, 曲凌雁. 城市旅游流网络结构特征及其影响因素——以上海市为例[J]. 世界地理研究, 2021, 30(1):114-124. |
| [LI Qian, QU Lingyan. The network structure and influencing factors of the tourist flow within the city:The case of Shanghai[J]. World Regional Studies, 2021, 30(1):114-124.] | |
| [32] | 刘洁君. 明清时期京杭大运河山东段沿线城市的空间形态研究[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2021. |
| [LIU Jiejun. Research on the Spatial Form of Cities along the Shandong Section of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal in Ming and Qing Dynasties[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong Jianzhu University, 2021.] | |
| [33] | 刘军. 整体网分析讲义:UCINET软件实用指南[M]. 上海: 格致出版社, 2009:127-129. |
| [LIU Jun. Lectures on Whole Network Approach:A Practical Guide to UCINET[M]. Shanghai: Truth & Wisdom Press, 2009:127-129.] | |
| [34] | 刘庆芳, 王兆峰. 生态环境质量对旅游效率的影响——基于长江经济带的实证分析[J]. 福建农林大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2021, 24(3):68-76. |
| [LIU Qingfang, WANG Zhaofeng. The impact of eco-environment quality on tourism efficiency:An empirical analysis based on the Yangtze River Economic Belt[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2021, 24(3):68-76.] | |
| [35] | 马丽君, 肖洋. 典型城市居民国内旅游流网络结构特征[J]. 经济地理, 2018, 38(2):197-205,219. |
| [MA Lijun, XIAO Yang. The structure characteristics of domestic tourist flow network in typical urban dweller[J]. Economic Geography, 2018, 38(2):197-205,219.] | |
| [36] | 施利锋, 黄贤金. 中国大运河沿线城市扩张时空差异研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(8):1206-1216. |
| [SHI Lifeng, HUANG Xianjin. Spatiotemporal differences of urban expansion along China’s Grand Canal[J]. Progress in Geography, 2019, 38(8):1206-1216.] | |
| [37] | 时少华, 李享. 传统村落旅游发展中信任与利益网络效应研究——以北京市爨底下村为例[J]. 旅游学刊, 2019, 34(9):30-45. |
| [SHI Shaohua, LI Xiang. Research on the effect of trust and interest network in the tourism development of traditional village:Take the Cuandixia village in Beijing as an example[J]. Tourism Tribune, 2019, 34(9):30-45.] | |
| [38] | 唐顺铁, 郭来喜. 旅游流体系研究[J]. 旅游学刊, 1998(3):38-41. |
| [TANG Shuntie, GUO Laixi. Research on tourism flow system[J]. Tourism Tribune, 1998(3):38-41.] | |
| [39] | 汪秋菊, 黄明, 刘宇. 城市旅游客流量—网络关注度空间分布特征与耦合分析[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2015, 31(5):102-106,127. |
| [WANG Qiuju, HUANG Ming, LIU Yu. Research on spatial feature and coupling correlation between urban tourist flow and network attention-degree[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2015, 31(5):102-106,127.] | |
| [40] | 王淑华, 董引引. 基于旅游数字足迹的河南省旅游流网络结构特征研究[J]. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(3):96-103,126. |
| [WANG Shuhua, DONG Yinyin. The structural characteristics of tourism flow network in Henan Province based on tourism digital footprint[J]. Journal of Northwest Normal University(Natural Science), 2021, 57(3):96-103,126.] | |
| [41] | 王晓芳, 郭艳, 李宇晟, 等. 多尺度视角下都市旅游流网络结构演化研究——以武汉市为例[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2023, 42(2):93-99. |
| [WANG Xiaofang, GUO Yan, LI Yusheng, et al. Evolutionary research on network structure of urban tourism flow from a multi-scale perspective:A case study of Wuhan City[J]. Areal Research and Development, 2023, 42(2):93-99.] | |
| [42] | 王永明, 王美霞, 吴殿廷, 等. 基于ZINB模型的中国省域间入境旅游流影响因素[J]. 经济地理, 2018, 38(11):234-240. |
| [WANG Yongming, WANG Meixia, WU Dianting, et al. Determinants of inbound tourism flows between provinces in China based on ZINB model[J]. Economic Geography, 2018, 38(11):234-240.] | |
| [43] | 王越乙, 徐枞巍. 指数随机图(p*)模型不同描述的对比研究[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 55(4):422-427. |
| [WANG Yueyi, XU Congwei. Comparative analysis of different descriptions in exponential random graph(p*)models[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science & Technology), 2015, 55(4):422-427.] | |
| [44] | 王兆峰, 张先甜. 黄河流域旅游经济系统韧性的时空差异特征及其影响因素[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2023, 39(3):112-121. |
| [WANG Zhaofeng, ZHANG Xiantian. Spatio-temporal differences and influencing factors of resilience of tourism economic system in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2023, 39(3):112-121.] | |
| [45] | 吴中堂, 刘建徽, 袁俊. 大陆居民赴台湾自由行旅游流网络分析及演化研究[J]. 旅游学刊, 2016, 31(10):113-121. |
| [WU Zhongtang, LIU Jianhui, YUAN Jun. Network analysis and evolutionary studies based on tourist flows of mainland residents’s self-service traveling in Taiwan[J]. Tourism Tribune, 2016, 31(10):113-121.] | |
| [46] | 徐敏, 黄震方, 曹芳东, 等. 基于在线预订数据分析的旅游流网络结构特征与影响因素——以长三角地区为例[J]. 经济地理, 2018, 38(6):193-202. |
| [XU Min, HUANG Zhenfang, CAO Fangdong, et al. The network structure features and influence factors of tourism flows based on online data analysis:Taking the Yangtze River Delta region as an example[J]. Economic Geography, 2018, 38(6):193-202.] | |
| [47] | 闫闪闪, 靳诚. 市域内部旅游流空间扩散动力机制——以洛阳市为例[J]. 人文地理, 2019, 34(5):149-158. |
| [YAN Shanshan, JIN Cheng. The dynamic mechanism of the city domestic tourist flow space:A case study of Luoyang[J]. Human Geography, 2019, 34(5):149-158.] | |
| [48] | 张昊, 韩增林, 乔国荣, 等. 黄河流域城市间旅游经济联系格局及影响因素研究[EB/OL].[2023-07-07]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail//65.1103.x.20230203.0913.001.html. |
| [ZHANG Hao, HAN Zenglin, QIAO Guorong, et al. The spatial connection pattern and influencing factors of tourism economy among cities in the Yellow River Basin[EB/OL].[2023-07-07]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail//65.1103.x.20230203.0913.001.html.] | |
| [49] | 邹统钎, 韩全, 常东芳. 基于地格理论的大运河国家文化公园旅游品牌基因研究[J]. 扬州大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2022, 26(2):101-113. |
| [ZOU Tongqian, HAN Quan, CHANG Dongfang. A research based on geo-grid theory on the tourism brand genes of the national grand canal cultural parks[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University(Humanities & Social Sciences), 2022, 26(2):101-113.] |
| [1] | 陆林, 陈劼绮, 毕珊珊, 许艳, 崔静, 方叶兵. 徽州村落旅游者乡愁感知及其影响因素研究[J]. 旅游导刊, 2023, 7(6): 59-76. |
| [2] | 朱鹤, 龙江智, 刘家明, 张书颖, 林诗然. 大数据应用视角下旅游流国际研究的进展与展望[J]. 旅游导刊, 2023, 7(3): 78-97. |
| [3] | 周波,肖洪根,叶顺. 国外旅游领域中的知识转移研究:述评与展望[J]. 旅游导刊, 2021, 5(5): 87-106. |
| [4] | 马丽君, 肖洋. 湖南省居民省内旅游流的集聚扩散时空特征——基于网络关注度数据的分析[J]. 旅游导刊, 2018, 2(2): 40-55. |
| [5] | 吴艺娟, 郑向敏. 旅游者安全行为外文研究文献综述[J]. 旅游导刊, 2017, 1(5): 68-85. |
| [6] | 邹永广, 林炜铃. “驴友”安全事故影响因素重要度评价研究[J]. 旅游导刊, 2017, 1(4): 57-70. |
| [7] | 唐健雄, 孙桥. 新常态下委托管理饭店知识转移的影响因素研究[J]. 旅游导刊, 2017, 1(2): 60-78. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
